Body composition is more than just a number on the scale. It tells you what your body is made of - fat, muscle, bone, and water. Unlike weight alone, it gives a clearer picture of your health and fitness.
Two people can weigh the same but have completely different body compositions. That is why it is so important to understand what is going on beneath the surface.
What Is Body Composition?
Your body is not just a lump of weight. It is a combination of fat, bone, muscle, water, and tissues, each playing a role in how you function. Knowing your body composition gives insight into your fitness level, overall health, and potential risks for diseases like diabetes or heart conditions.
A scale can’t tell you that, but body composition can.

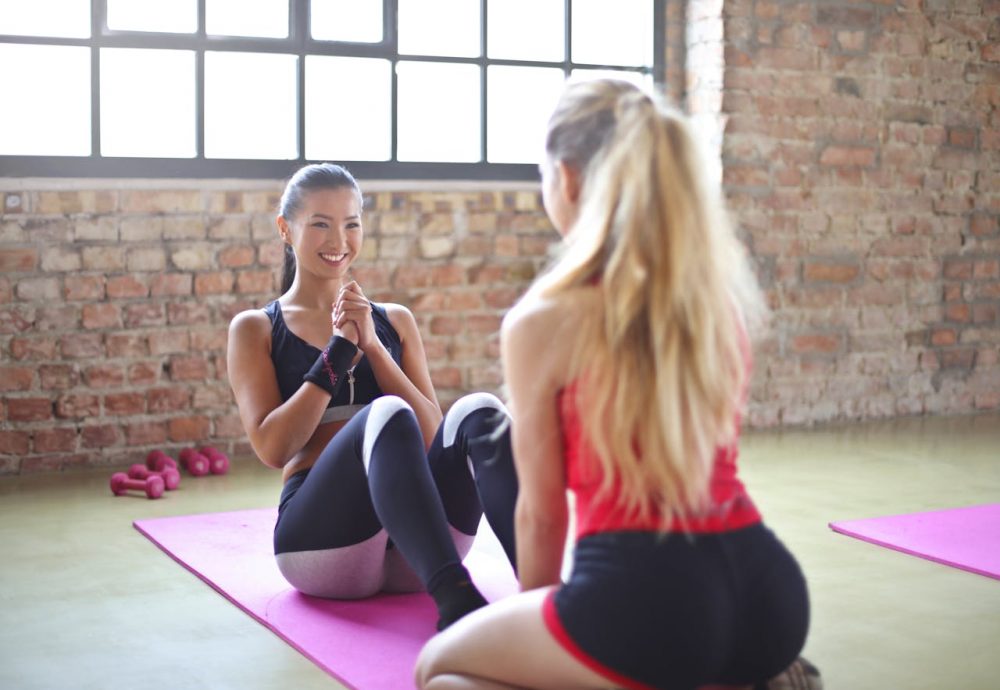
Master / Pexels / A person weighing 170 pounds with 20% body fat has a very different body makeup than someone of the same weight with 30% body fat.
Notice, the lower-fat individual has more muscle, which means better strength, endurance, and metabolism. Understanding these numbers helps tailor fitness and nutrition plans to reach specific health goals.
What Can Body Composition Tell You About Your Health?
It is not just about looking fit. Instead, it is about being fit from the inside out. High body fat percentages can signal a risk for conditions like obesity, heart disease, and metabolic disorders. On the other hand, too little body fat can lead to hormonal imbalances and weaker immunity.
Muscle mass is another crucial factor. More lean muscle means higher metabolism, stronger bones, and better physical performance. Even hydration levels play a role. Too little water retention could indicate dehydration, while excess water weight might hint at inflammation or kidney issues.
When you know your body composition, you understand what your body truly needs.
How Do You Measure Body Composition?
Stepping on a regular scale won’t give you the full picture. Body composition is measured using specialized tools and techniques. One of the most common methods is bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), found in many smart scales and gym devices.
It sends a weak electrical current through your body to estimate fat and lean mass percentages.

Cowley / Pexels / For more precision, methods like dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans and hydrostatic weighing provide accurate breakdowns.
Skinfold calipers, though old-school, can also offer rough estimates. If you want to truly understand your body composition, using these tools regularly can help track progress over time.
How Can You Improve Your Body Composition?
A balanced diet and regular exercise are key to a better body composition. Strength training helps build lean muscle, while cardiovascular exercises burn fat. A mix of both works best for long-term results. Crash diets might lower weight, but they often strip away muscle instead of fat.
Eating enough protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs fuels your body while keeping it lean. Sleep and stress management also impact body composition. Poor sleep and high stress can lead to fat storage and muscle loss.
Remember, it is not just about working out. It is about creating a lifestyle that supports a strong, healthy body.
Body Composition Matters More Than BMI
Body mass index (BMI) is often used to measure health, but it doesn’t tell the whole story. A muscular person could have a high BMI but low body fat, while someone with a normal BMI could carry excess fat and little muscle. This makes BMI an unreliable way to assess health.
Body composition, on the other hand, looks at what your body is actually made of. It provides a clearer picture of whether you need to gain muscle, lose fat, or simply maintain your current balance. Focusing on these numbers rather than BMI alone helps create a smarter approach to fitness and nutrition.