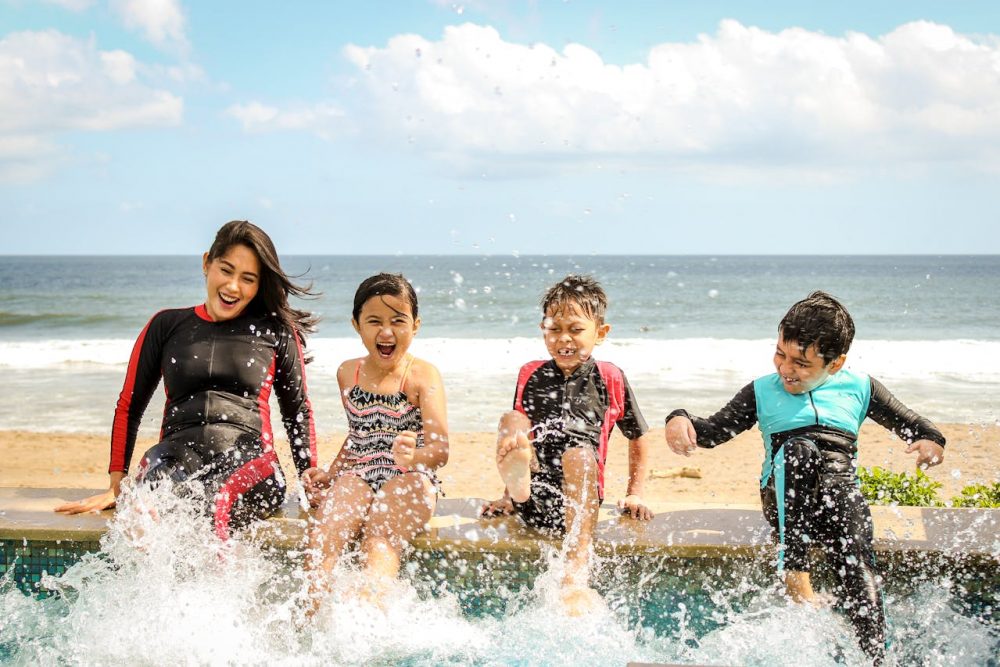
Whether you are a competitive swimmer or just love to swim for fun, increasing your lung capacity can dramatically improve your performance. With better lung capacity, you will swim longer distances, maintain faster speeds, and feel less fatigued. But how can lung capacity for swimming be increased? Well, the key is understanding that increasing lung capacity is not just about swimming more.
It involves strategic training, good nutrition, and a step-by-step approach. So, how can you do it?
Practice Breath Control
How to increase lung capacity for swimming? To begin with, practice breath control. When you swim, timing your breaths and knowing how to manage them is crucial. Begin by practicing holding your breath underwater. Start with shorter periods and gradually increase the time.
You can practice this either in the pool or on land by taking a deep breath, holding it for as long as comfortable, and then slowly exhaling. Over time, this will train your lungs to adapt to longer durations without air, helping you in the water.
Building Up Slowly
It can be tempting to push yourself hard right away when working on lung capacity. But pacing is essential. Start small and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercises. For example, if you are practicing holding your breath, try adding a few extra seconds each time.
Slowly increasing the demand on your lungs allows them to adapt and grow stronger over time without causing strain or discomfort.

Jim / Pexels / Overworking your lungs too quickly can lead to dizziness, fatigue, or worse, make you lose confidence. Swimming is about consistency.
So, it is better to add small increments and train regularly than to push yourself to the limit in a single session. Over time, you will notice significant improvements in your lung capacity, making your swims smoother and more enjoyable.
Focus on Your Posture
Believe it or not, your body position plays a crucial role in how to increase lung capacity for swimming. Poor posture can restrict your breathing. Whether you are sitting at a desk, standing, or swimming, maintaining good posture allows your lungs to expand fully.
When you are hunched over or tense, your chest cavity is compressed. This limits the amount of air your lungs can take in.
In swimming, streamlined body positioning is essential for reducing drag and improving lung capacity. Make sure your head is in line with your body, your spine is straight, and your core is engaged. This will open up your chest and allow more room for your lungs to expand.
Strengthen Your Core and Diaphragm
Your diaphragm is a key muscle in controlling your breathing, and by training it, you can improve how efficiently you use air. Diaphragmatic breathing exercises, such as taking deep breaths where your belly rises and falls, can help train this muscle.
Plus, focusing on core strength will improve your stability in the water, allowing you to swim more efficiently without wasting energy on maintaining balance.

Pixabay / Pexels / Strengthening your diaphragm and core muscles is another effective way to increase lung capacity for swimming.
A strong core also supports better breathing by stabilizing your torso, allowing your lungs to fully expand. Planks, sit-ups, and other core exercises can enhance this stability. If you make core and diaphragm exercises a regular part of your training routine, you will not only increase your lung capacity! You will also improve your overall swimming technique.
Eat Right and Stay Hydrated
Your body needs the right fuel to perform at its best, and that includes your lungs. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals helps reduce inflammation in the body, including the lungs.
Foods high in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, berries, and nuts, can help support lung function and overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, are also beneficial for lung health.